QRadar vs. Splunk (2023): SIEM Tool Comparison
This is a comprehensive QRadar vs. Splunk SIEM tool comparison, covering their features, pricing, and more. Use this guide to find the best SIEM tool for you.
Security information and event management (SIEM) solutions play a major role in organizations’ cybersecurity architecture. SIEM tools provide organizations a way to identify, monitor, analyze and respond to security events that can compromise business applications, networks, endpoints and cloud environments. While there are quite a number of SIEM tools available to businesses, IBM QRadar and Splunk Enterprise Security rank among the biggest names in the market. However, there are other SIEM tools on the market. But what distincts one solution from the other? This head-to-head comparison of QRadar vs Splunk outlines the differences and similarities between both SIEM tools.
Jump to:
QRadar vs. Splunk: Comparison table
The following table summarizes how each SIEM solution compares to the other in key areas.
| Features | QRadar | Splunk |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized dashboard | Yes | Yes |
| Integrations | About 700 integrations | Over 2,300 integrations |
| Threat intelligence | Yes | Yes |
| Cloud migration support | Yes | Yes |
| Deployment options | SaaS, Software and Managed service | Cloud, on-premises or hybrid |
| Free trial | No. But, you can request for demo | Yes |
Featured Partners
QRadar vs Splunk: Pricing
QRadar offers different pricing options based on consumption metrics and nature of deployment.
- The usage model: This pricing model is based on the number of log events ingested per second, also known as Events per Second (EPS) and on the network communications per minute or Flows per Minute (FPM).
- The Enterprise model: Under this model, users are charged based on the number of Managed Virtual Servers (MVS) consumed.
In addition, customers using QRadar on-premise can either pay by subscription or perpetual licensing. Users running the tool as SaaS deployments can only go with the subscription model.
Similar to QRadar, Splunk also offers a flexible pricing model that caters to different customer needs. Billing is according to the models captured below.
- Workload model: Here, customers are billed based on the specific types of workloads they run.
- Ingest model: Pricing is determined by the volume of data ingested into the Splunk Platform.
- Entity model: This is structured around the number of hosts utilizing Splunk.
- Activity-based: Customers are charged based on the specific activities, events, or logs that are being tracked and analyzed within the Splunk Platform.
To get specific pricing quotes, we recommend getting in touch with the vendors.
Feature comparison: QRadar vs. Splunk
This section provides an in-depth comparison of some features found in both solutions.
Integrations
QRadar offers over 700 integrations. The solution recently expanded its offering by adding Red Hat OpenShift to its stack, a feature that simplifies deploying and managing hybrid infrastructures.
There is also the integration of device support modules (DSM), network behavior collection devices, threat intelligence feeds, and vulnerability scanners and other integrations with other IBM and third-party tools. Other notable integrations include Microsoft 365 Defender, IBM Randori Recon, etc.
With over 2300 integrations, Splunk offers more integrations than QRadar and works well with a wide range of software products by third-party companies. Splunk’s notable integrations include AWS, Azure, MongoDB, Google Cloud Platform, Kubernetes, OpenShift, etc.
Deployment options
QRadar can be deployed as software, SaaS or via managed services. As software, QRadar is available as a hardware or virtual appliance product that can be deployed on-premise or in the cloud. With the SaaS deployment option, IBM runs and maintains the entire infrastructure, including implementing patches and other relevant updates.
Splunk users can deploy the solution as a distributed search or a single instance deployment. It is also offered as both a cloud platform and an on-premise solution.
Analytics and reporting
IBM QRadar uses User Behavior Analytics application to analyze users’ behavior on an organization’s internal network and point out risks where necessary. Analytics in QRadar is also automated by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), and reports and alerts are automatically provided based on potential risks found.
Figure A
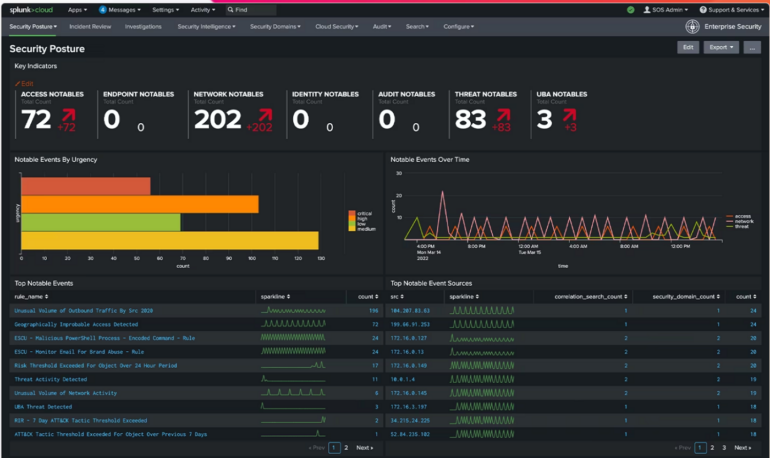
On analytics and reporting, Splunk uses a data analytic engine to collect and analyze data from different environments and formats. A Security Posture dashboard also provides real-time analytics into events across all environments. Splunk also offers customizable reporting features that allow users to clone reports, and edit reports’ permissions, descriptions and schedules.
Figure B
Incident response and automation
QRadar offers built-in incident response capabilities that streamline the process of handling security incidents. It provides automated response actions based on predefined playbooks. This allows organizations to define and execute a series of actions in response to specific security events.
Figure C
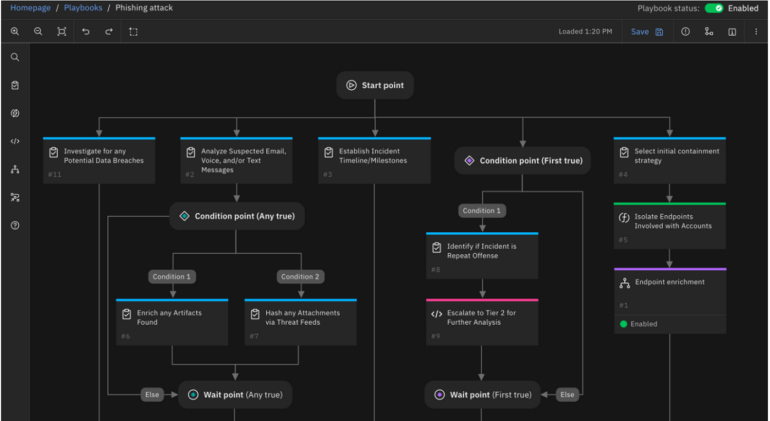
Similarly, Splunk offers automation and orchestration capabilities through its Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platform, Splunk Phantom. While this feature is a standalone tool, it is usually deployed alongside SIEM tools as it helps organizations automate incident response actions faster.
Ease of use
While QRadar is easier to set up and deploy, it’s not as user-friendly once you get it up and running. The user interface for QRadar can feel a bit outdated and is not as intuitive as some of the other offerings on the market. Users say that the modules often feel cobbled together from different products instead of presenting a consistent look and feel, which affects the user experience.
Splunk makes up for its more difficult deployment with a user interface that is easy to navigate and understand. Users praise the self-explanatory navigation and the appealing graphics and layout, which are easy even for those without as much SIEM or technical experience to navigate.
QRadar Pros and Cons
Captured below are the advantages and disadvantages of using QRadar.
Pros
- Easy to deploy.
- Great reporting features.
- Automates threat detection and prioritization.
- Complex algorithms to calculate and prioritize threats.
- Automates compliance.
Cons
- Complicated payment plan.
- Integration is not as broad as Splunk’s.
- Absence of free trial.
Splunk Pros and Cons
Highlighted below are some key takeaways and drawbacks of Splunk.
Pros
- Robust log analysis for effective management features.
- Over 2,300 integrations.
- Automated risk-based alerting.
- Over 50 free training courses and certifications.
- 60-day free trial available.
Cons
- Not easy to deploy.
- Lacks adequate pricing information.
Methodology
To draw a valid comparison between the two SIEM tools, we prioritized features like user-friendliness, integration capabilities, threat analysis and reporting, deployment methods and pricing models. We also checked out user reviews on Gartner Peer Insight for third-party opinions. This method allowed us to combine information from our research with what users say about each product to compare both SIEM solutions.
Should your organization use QRadar or Splunk?
Both QRadar and Splunk bring strengths and weaknesses. While QRadar is easier to deploy, it falls short when it comes to user-friendliness as well as available integrations. If you already use a lot of IBM enterprise software offerings, it may be worth taking a look at QRadar since it will definitely integrate well with that stack.
Meanwhile, Splunk is more difficult to deploy but offers a better user interface and more integrations. So, if you use software products from different companies, Splunk may be a better shot. As for the pricing, both QRadar and Splunk calculate the cost differently based on different consumption metrics and data, so it’s hard to make a direct comparison without knowing your specific company needs. Users note that prices for both services are high compared to competitors, so if you are looking for a more cost-effective option, you may find one in our comprehensive review of the top SIEM tools in the market.
Source: News
